Resources for Factorising Expressions
-
Questions
21
With Worked SolutionClick Here -
Video Tutorials
2
Click Here
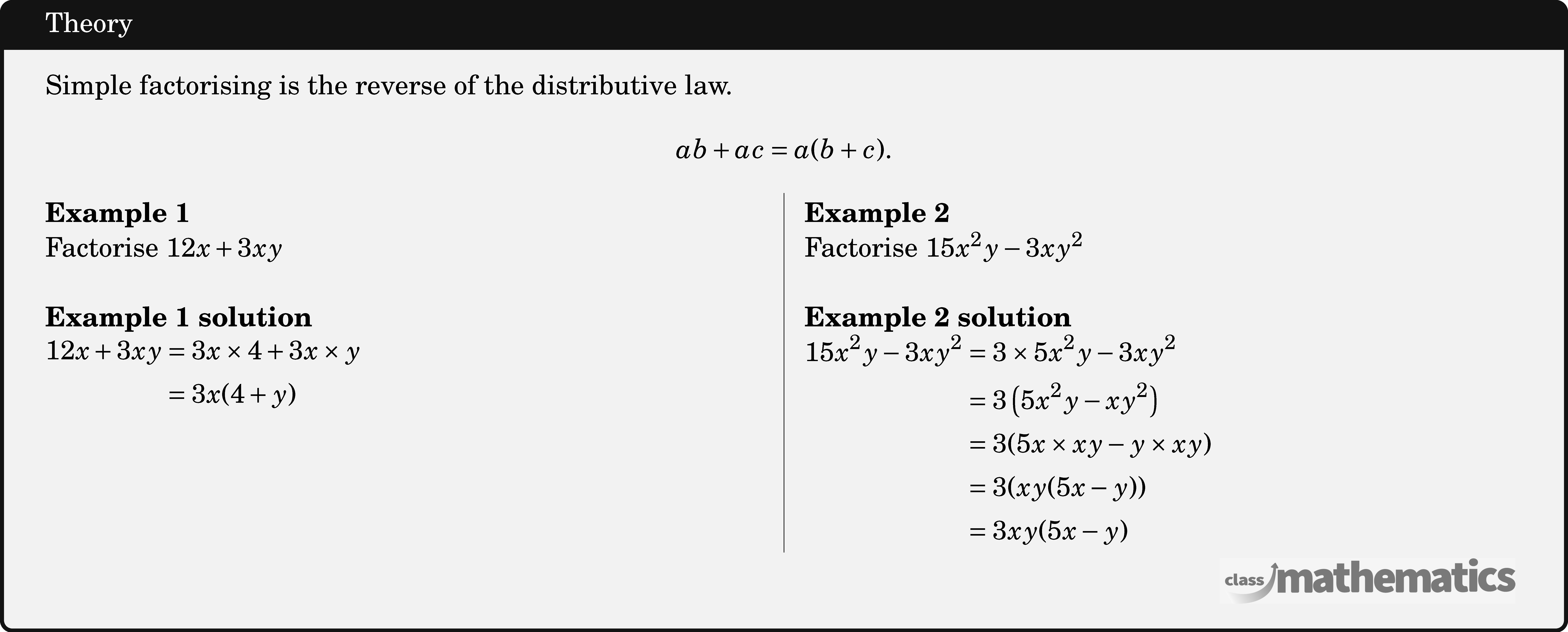
Factorising Expressions Theory
21
With Worked Solution2

Videos relating to Factorising Expressions.
With all subscriptions, you will receive the below benefits and unlock all answers and fully worked solutions.