Resources for Applications of the Dot Product
-
Questions
7
With Worked SolutionClick Here -
Video Tutorials
1
Click Here -
HSC Questions
7
With Worked SolutionClick Here
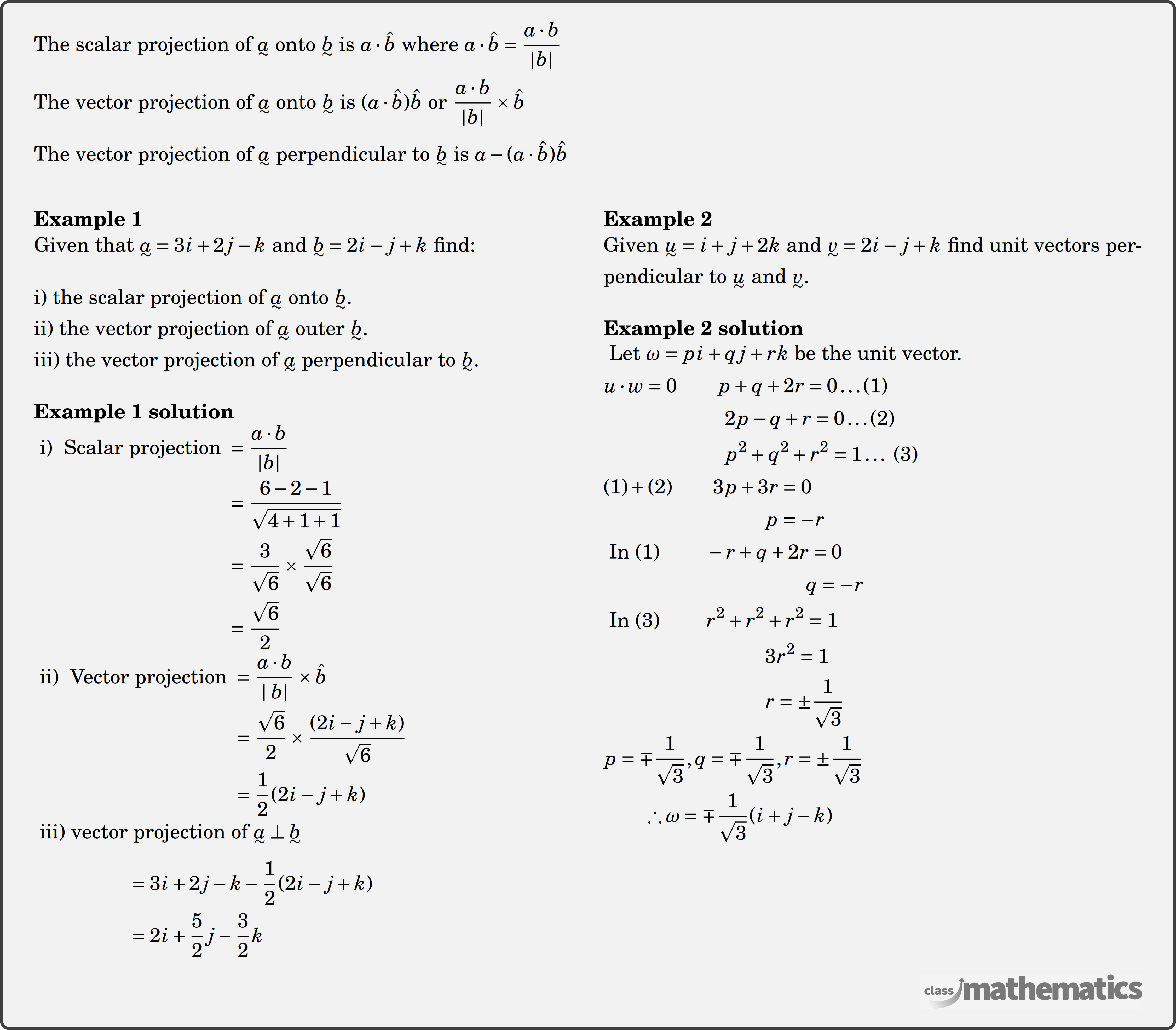
Applications of the Dot Product Theory