Resources for Energy Consumption
-
Questions
9
With Worked SolutionClick Here -
Video Tutorials
3
Click Here
Energy Consumption Theory
9
With Worked Solution3

Videos relating to Energy Consumption.
With all subscriptions, you will receive the below benefits and unlock all answers and fully worked solutions.
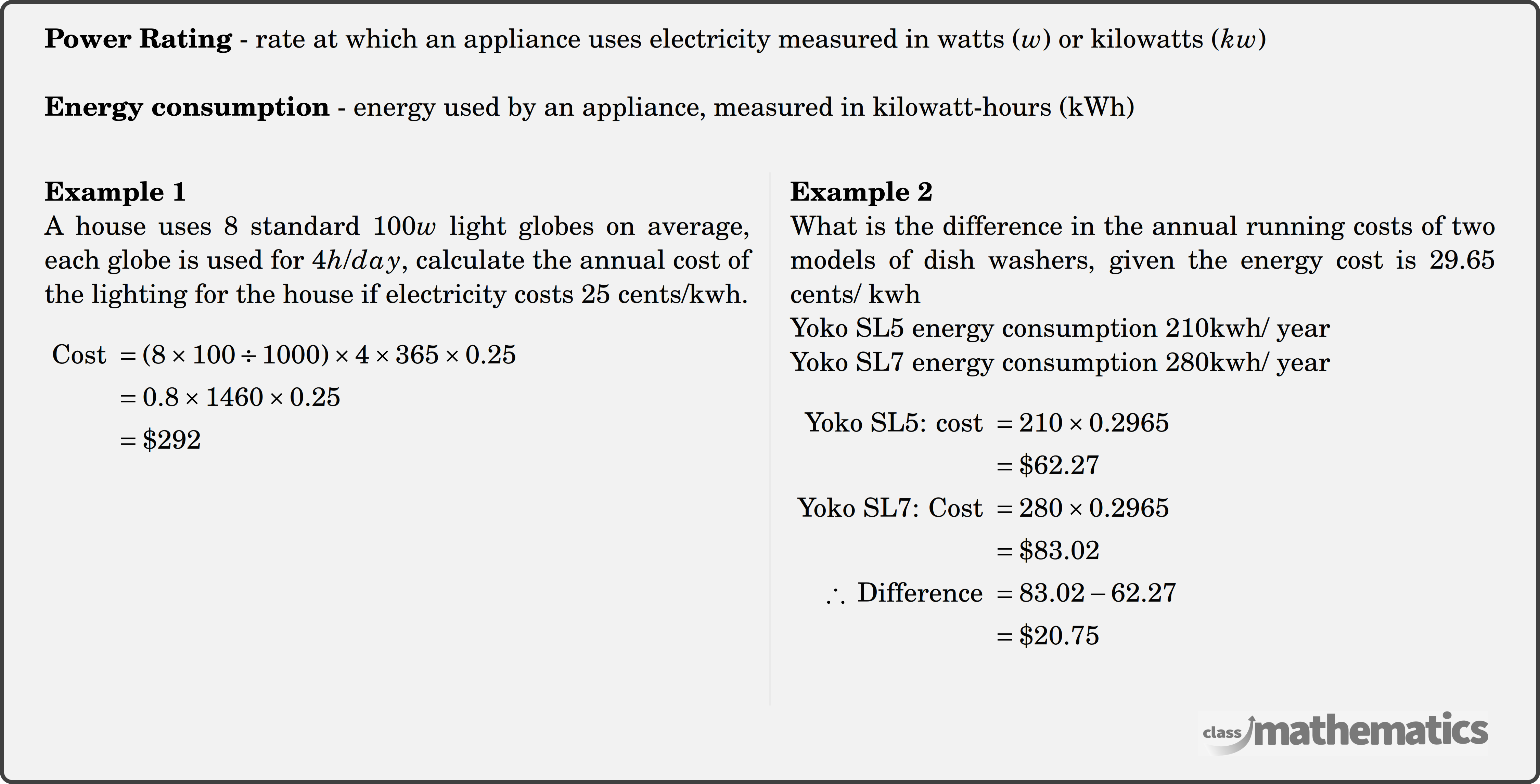
Energy Consumption
Power is the rate at which energy is consumed, we measure it in watts (W). For example, a heater has a power rating of 2000W while an LED light bulb might only use 10W.
\[\begin{array}{ | c | c | c | }\hline \text{Name} & \text{Amount} & \text{Example} \\
\hline \text{milliwatt (mW)} & \text{1/1000th of a watt} & \text{hearing aid} \\
\hline \text{watt (W)} & \text{one watt} & \text{LED bulb} \\
\hline \text{kilowatt (kW)} & \text{1000 watts} & \text{small electric heater} \\
\hline \text{megawatt (MW)} & \text{1 million watts} & \text{submarine} \\
\hline \text{gigawatt (GW)} & \text{1 billion watts} & \text{power plant} \\
\hline \end{array}\]
Kilowatt-hours (kWh)
When we pay for electricity it is not enough to know how many watts each appliance uses, we need to know how long they have been running for. For example a 2kW heater will use 2kWh in 1 hour or 4kWh in 2 hours. The amount of kilowatt-hours we use will determine the cost of our electricity bill.
We have all seen energy rating stickers like the one to the right on our electrical appliances. What we learn from the sticker to the right is that this washing machine will use on average 399kWh per year if you use the warm wash.
